OpenXGR User Manual
2023-04-23
Section 1 OVERVIEW

FIGURE 1.1: The logo for OpenXGR.
Motivation
We are very pleased to introduce an updated version of our XGR software, which has gained increasing popularity in genomic summary data interpretation since its first release (see Genome Medicine 2016). This update features a newly designed web server, called OpenXGR, now made available here to all users for free and without any login requirements. It enables almost real-time enrichment and subnetwork analyses for a user-input list of genes, SNPs, or genomic regions, leveraging ontologies, networks, and knowledgebase resources about functional genomic datasets, such as e/pQTL, promoter capture Hi-C, and enhancer-gene maps. Besides, the web server is user-friendly, very suitable for users who are unfamiliar with coding.
One of the major challenges in genomics research is how to bridge the gap between generated genomic summary data and downstream knowledge discovery. We define genomic summary data as a list of genes or SNPs (more generally, genomic regions), along with their significance levels (e.g. p-values). We are leading the field in making sense of genomic summary data for knowledge discovery through developing approaches and tools that have been verified to be efficient and effective, including XGR (see Genome Medicine 2016), dnet (see Genome Medicine 2014), Priority index (see Nature Genetics 2019), and dcGO (see Nucleic Acids Research 2013).
Building upon our previous approaches that have stood the test of time (with most of citations received in the past two years), and also incorporating the growing knowledgebase of ontologies and networks, OpenXGR offers six analysers for enrichment and subnetwork analyses, each doing specific interpretations tailored to genomic summary data at the gene, SNP, and genomic region levels.
Enrichment Analysers
ENRICHMENT ANALYSER (GENES) - EAG, identifies ontology terms enriched for input genes; see Example Output
ENRICHMENT ANALYSER (SNPS) - EAS, identifies ontology terms enriched for genes linked from input SNPs; see Example Output
ENRICHMENT ANALYSER (REGIONS) - EAR, identifies ontology terms enriched for genes linked from input genomic regions; see Example Output
Subnetwork Analysers
SUBNETWORK ANALYSER (GENES) - SAG, identifies a gene subnetwork based on input gene-level summary data; see Example Output
SUBNETWORK ANALYSER (SNPS) - SAS, identifies a gene subnetwork based on genes linked from input SNP-level summary data; see Example Output
SUBNETWORK ANALYSER (REGIONS) - SAR, identifies a gene subnetwork based on genes linked from input genomic region-level summary data; see Example Output
Primary Data Sources
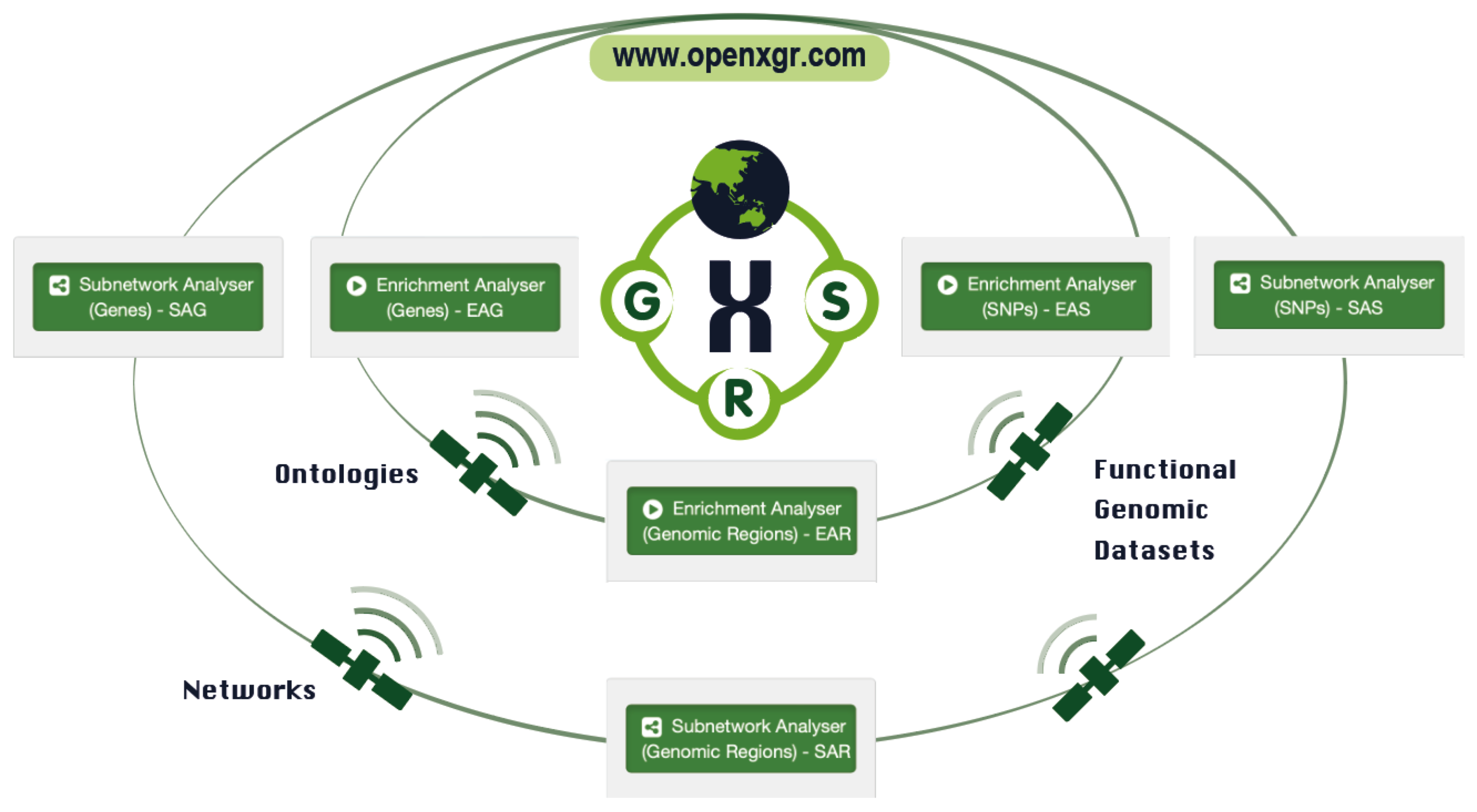
FIGURE 1.2: The OpenXGR web server is depicted as our ‘Earth’ in the sense that it comprises six analysers designed to interpret summary-level genomic data related to genes (G), SNPs (S), and genomic regions (R). Similar to satellites that orbit our planet and provide real-time information, OpenXGR leverages knowledgebase on ontologies, networks, and functional genomic datasets to enable real-time enrichment and subnetwork analyses.